Source: enterprisetalk.com
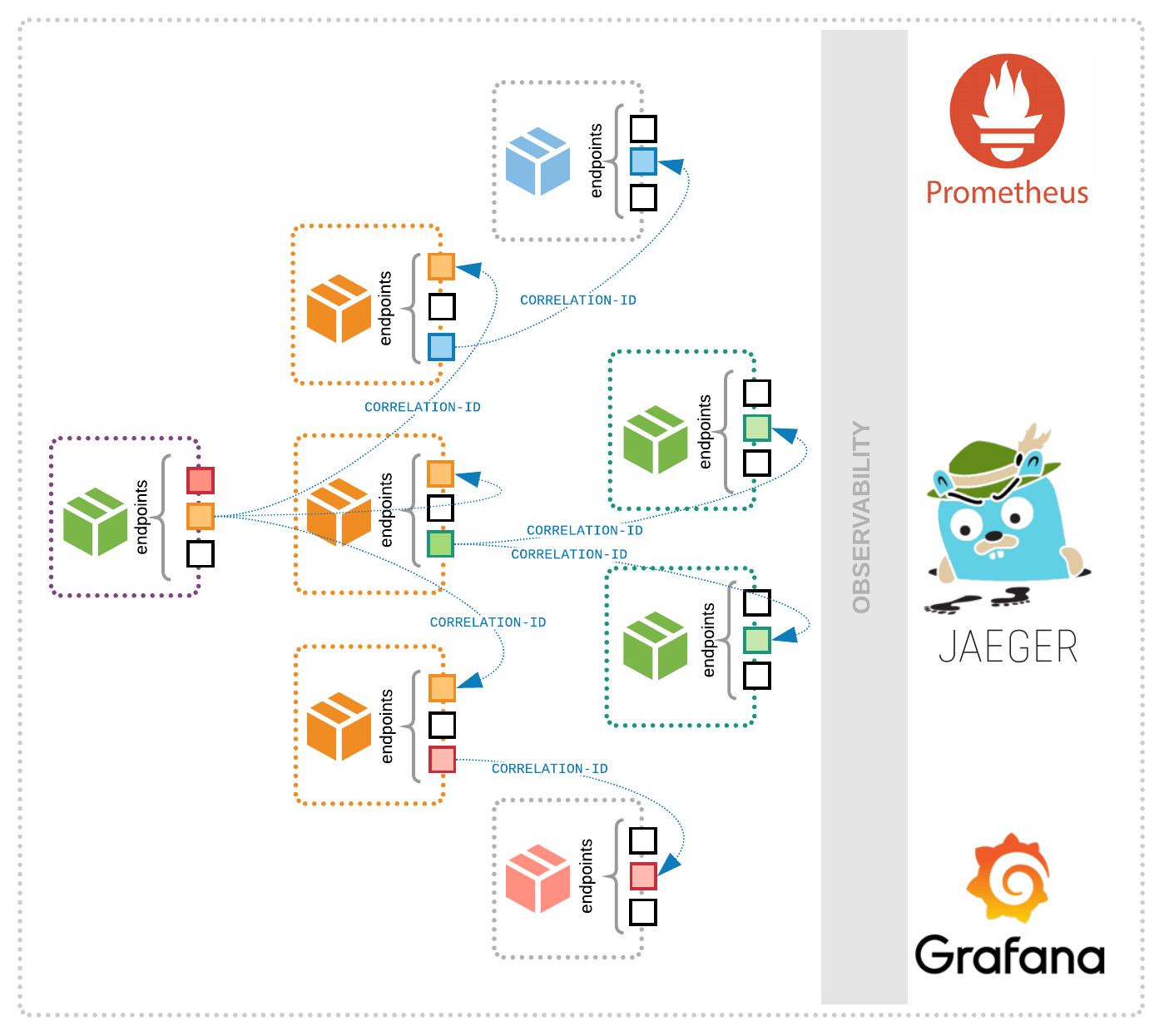
Microservice architecture works on the principle of displaying only the relevant details to the end-user. It conceals the complexities associated with software and hardware, operating systems, and development toolkits inside a standard service available to employees on network.
IT personnel refer to this functionality as an “abstraction layer”. If an employee is using a certain application and even if its vendors completely modify the physical location of the data center, hardware, or the programing language, the productivity of the application will not be affected in any manner. CIOs will find that for an internal software application, they no longer have to worry about the time-consuming and expensive labor of rewriting complex connections and interfaces between systems when using microservice architecture. The architecture runs on a standardized order management process and will deliver the exact results regardless of the application used, and the shift to a different platform will be seamless for any application that uses the service.
Best ways to implement a microservice architecture
IT leaders state that the best way to integrate the service is by using them in the organization’s service architecture. Most business applications and modern end-user applications are high-level logic and end-user interface that interacts via multiple microservices.
CIOs must be aware that these services require keys or registration and some services require payment after a point. This investment is however, less compared to building custom codes and maintaining them. Employees working on building microservices can identify the key services that the organization can deploy either externally or internally. Some examples of internal microservice include customer information that can be utilized by the organization’s customer support team, call center, and logistics application.
Microservices as a part of the technology tack
CIOs acknowledge that microservices have leveled the technology playing area to a huge extent. They are considering investing in it, as a measure to decrease the dependency on the legacy and proprietary systems. Using internal microservices ensures that organizations are independent of particular software or hardware third-party vendor and can easily upgrade parts of the infrastructure without affecting other applications.
Many IT leaders have put the concept of exploring microservices on hold as they consider the idea to be confusing and complex, but the service is pretty easy to be implemented.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687 |
+91 8409492687 |  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com