Source: beebom.com
Google’s AI research team has developed a new machine learning system that they call “Form2Fit” in collaboration with researchers from Stanford University and Columbia University. The project makes use of deep neural networks to teach a robot arm to recognize and assemble objects.
“If robots could learn “how things fit together,” then perhaps they could become more adaptable to new manipulation tasks involving objects they have never seen before, like reconnecting severed pipes, or building makeshift shelters by piecing together debris during disaster response scenarios.”, wrote Kevin Zakka, Research Intern and Andy Zeng, Research Scientist in a blog post.
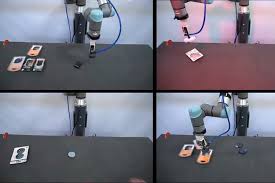
The researchers tested Form2Fit in a robot to evaluate the efficiency of the algorithm. In the test, the robot was assigned to assemble objects into a blister pack. After the testing process, the researchers noted a 94% success rate with the algorithm. Notably, the system was able to fit objects that were not seen during the training process with an 86% success rate which represents the capability of the AI.
To put it in a more technical point of view, Form2Fit uses a two-stream matching network that infers “orientation-sensitive geometric pixel-wise descriptors”. The descriptors act as compressed 3D point representations that establish a connection with object geometry, textures, and contextual task-level knowledge. The picked objects will be rotated accordingly to fit the target location, thanks to the orientation-sensitive nature of the descriptors.
Take a look at the assembly robot trained by Form2Fit in the below GIF.
In our experiments, we assume a 2D planar workspace to constrain the kit assembly task so that it can be solved by sequencing top-down picking and placing actions. This may not work for all cases of assembly – for example, when a peg needs to be precisely inserted at a 45-degree angle. It would be interesting to expand Form2Fit to more complex action representations for 3D assembly”, concluded the researchers.
Check out the research paper of this project here and let us know the potential applications that come to your mind for using this algorithm in the comments.