Source: infoq.com
Uber andOpenAI have open-sourced Fiber, a new library which aims to empower users in implementing large-scale machine learning computation on computer clusters. The main objectives of the library are to leverage heterogeneous computing hardware, dynamically scale algorithms, and reduce the burden on engineers implementing complex algorithms on clusters.
It’s a challenge for machine learning frameworks to remain flexible enough to support reinforcement learning- (RL) and population-based algorithms together with other heuristics like deep learning because the requirements can vary greatly. While established frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch cover the setup of distributed training for most common machine learning methods, these frameworks are less fit for RL-based and population-based methods, which often require frequent interaction with simulators and a complex and dynamic scaling strategy. Fiber provides a unified Python user interface to its distributed computing framework to support these new requirements.
The research paper published alongside Fiber details the experiments used to evaluate the library on framework overhead, evolution strategies, and proximal policy optimization (PPO). Researchers compared Fiber with IPyParallel (iPython for parallel computing), spark, and the standard python multiprocessing library on framework overhead and found that Fiber outperforms iPyParallel and Spark when task duration is short, which is an important metric to understand when dealing with simulators. The performance of the distributed version of PPO enabled by Fiber compared with a multiprocessing implementation on Breakout in the Atari benchmark shows that Fiber can scale RL algorithms beyond local machines.
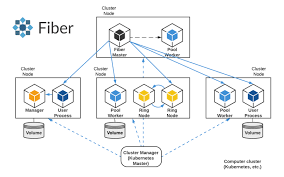
Fiber is split into the API layer, the backend layer, and the cluster layer. The API layer has similar requirements and semantics to the standard Python multiprocessing module, but it is extended to work in distributed environments. The backend layer can handle communication of tasks for a multitude of different cluster managers. Finally, the cluster layer contains the cluster managers like Kubernetes and Peloton.
Fiber introduces a new concept called job-backed processes. When starting one of these processes, a new job with a Fiber backend on the current cluster is created. A parent container encapsulates the required files, input data, and any other dependencies of that job before child processes are started with the same container image to guarantee a consistent running environment. The diagram below illustrates this architecture in more detail:
The recent releases of both Fiber and Google’s new distributed reinforcement learning library Seed RL show that big tech firms are aiming to both reduce costs and simplify the process for training cutting-edge machine learning algorithms.