
Introduction to SEO
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of improving your website to increase its visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). In simple terms, it’s about getting people to find your website when they search for something on Google, Bing, or other search engines.
HTML, the standard markup language for creating web pages, plays a significant role in implementing SEO strategies.
Here are some types of SEO and how HTML is involved:
1. On-Page SEO:
On-page SEO refers to the practice of optimizing the content and structure of your individual web pages to improve their ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). This involves optimizing various elements within your HTML code, including:
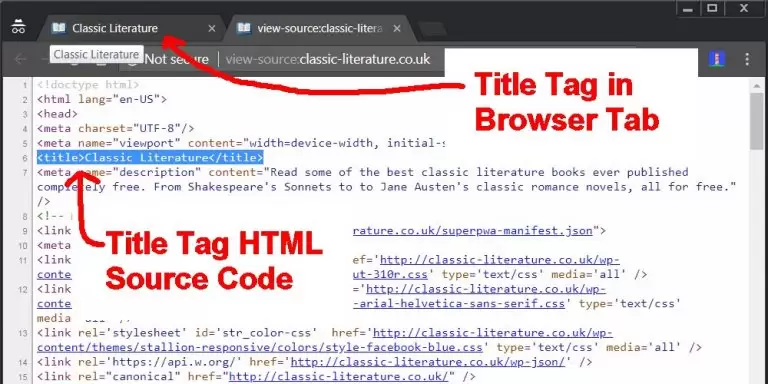
- Title Tags:
- The title tag is the most important on-page SEO element.
- It displays as the clickable headline in search engine results, so it needs to be informative, relevant to your target keyword, and entice users to click through.
- Aim for a length of around 50-60 characters, and include your target keyword naturally within the title.
2. Meta Descriptions:
- The meta description is a brief snippet of text that appears under the title tag in search results.
- While not directly a ranking factor, it can significantly impact click-through rates.
- Write compelling meta descriptions that accurately summarize your page content and encourage users to click through.
- Keep your meta descriptions under 160 characters.

3. Headings:
- Headings (H1 to H6 tags) structure your content and improve readability.
- Search engines consider headings when understanding your page content and its relevance to search queries.
- Use relevant keywords naturally within your headings, and ensure they accurately reflect the content structure.

4. Image Alt Text:
- Alt text provides a brief description of an image for users who cannot see it due to visual impairments or slow internet connections.
- Search engines also use alt text to understand the content of the image and its relevance to your page.
- Include relevant keywords naturally in your alt text, but avoid keyword stuffing.
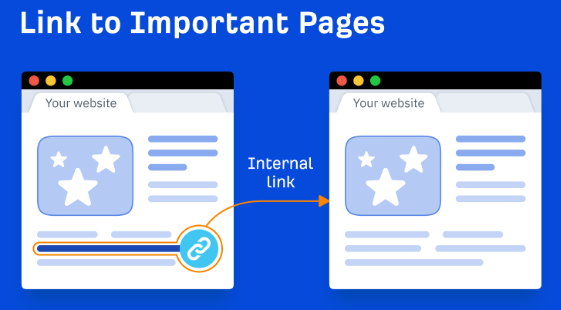
5. Internal Linking:
- Internal links connect your web pages, improving website navigation and user experience.
- Search engines also use these links to crawl and understand your website structure.
- Link relevant pages together using descriptive anchor text that includes your target keywords.
6. URL Structure: A clean and descriptive URL with relevant keywords can improve both user experience and search engine visibility.
7. Head element: Include relevant keywords in the meta keywords and meta robots tags.
8. Open Graph tags: Provide information for social media platforms.
9. Schema markup: Structured data for better search engine understanding and potential rich snippets.
2. Technical SEO
This focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of your website, including:
- Website speed: Optimize loading times for better user experience and SEO ranking.
- Mobile-friendliness: Ensure your website renders well on all devices.
- Structured data: Use schema markup to provide additional information to search engines.
- Crawlability and indexability: Make your website easily accessible to search engine crawlers.
- SSL certificate: Secure your website and build trust with users.
3. Off-page SEO
This focuses on efforts outside your website to improve its ranking, including:
- Backlinks: Building high-quality backlinks from other websites to your own.
- Local SEO: Optimizing your website for local search results if you have a physical location.
- Social media: Promoting your website content on social media platforms.
- Brand mentions: Building brand awareness through online mentions.
By understanding the basics of SEO and implementing effective strategies, you can take control of your website’s online presence and drive significant results for your business.