
What is SQLite?
SQLite is a popular lightweight, self-contained, serverless, and open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). It’s known for its simplicity, small footprint, and ease of use. Unlike client-server databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL, SQLite operates as a library that applications directly interact with, allowing users to create, read, update, and delete data using SQL queries.
What is top use cases of SQLite?
Top Use Cases:
- Mobile and Embedded Systems: Its minimal footprint and self-contained nature make it ideal for resource-constrained environments like mobile apps and embedded devices.
- Desktop Applications: Many desktop applications use SQLite for local data storage, like storing application settings, offline data, or user preferences.
- Prototyping and Experimentation: Due to its ease of use and quick setup, SQLite is a go-to for prototyping databases and experimenting with data structures before scaling to larger database systems.
- Web Applications: While not suitable for large-scale web applications, SQLite can be used for smaller web projects or local storage within browser extensions.
What are feature of SQLite?

Here are some features of SQLite is
- Simplicity and Ease of Use: SQLite requires minimal configuration and setup. You can start using it within your code with readily available libraries and tools.
- Lightweight and Efficient: Its small footprint makes it ideal for resource-constrained environments. It consumes minimal memory and runs efficiently with low overhead.
- ACID Transactions: SQLite ensures data integrity with full ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) compliance, guaranteeing reliable data updates even in case of errors or crashes.
- SQL Compatibility: SQLite uses a subset of the standard SQL language, making it familiar and easy to learn for developers who already know SQL.
- Cross-Platform: SQLite runs on all major operating systems, making it versatile for various development scenarios.
What is the workflow of SQLite?
The typical workflow with SQLite involves the following steps:
- Create or open a database file.
- Design a schema and create tables.
- Insert, update, or delete data using SQL commands.
- Query the database to retrieve or modify data as needed.
- Close the database after finishing the operations.
How SQLite Works & Architecture?
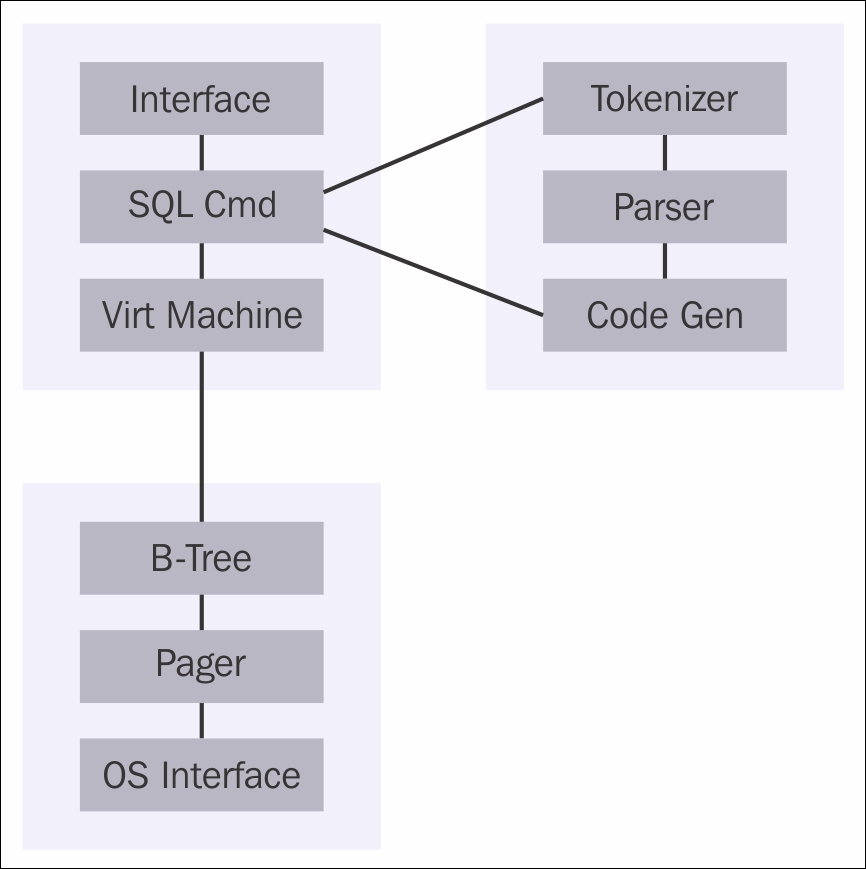
SQLite operates in three main stages: parsing, planning, and execution. Here’s a breakdown with a diagram:
- Parsing:
- Interface: Receives user input (SQL statements).
- Tokenizer: Breaks down the SQL into tokens (keywords, identifiers, numbers, etc.).
- Parser: Constructs a parse tree based on the tokenized structure.
2. Planning:
- Code Generator: Analyzes the parse tree and generates bytecode instructions.
- Query Planner: Determines the optimal execution strategy for the bytecode.
3. Execution:
Virtual Machine: Executes the bytecode instructions, accessing data through the following components:
- B-Tree: Stores data in a self-balancing tree structure for efficient retrieval.
- Page Cache: Maintains frequently accessed data in memory for faster retrieval.
- OS Interface: Interacts with the operating system for file I/O operations.
Key Points:
- SQLite uses a bytecode-based virtual machine for flexible execution.
- The B-tree structure ensures efficient data access and retrieval.
- The page cache optimizes performance by keeping frequently accessed data in memory.
- SQLite interacts directly with the operating system for file I/O.