
What is windows?
Windows is a graphical operating system developed by Microsoft. It is the most popular operating system in the world, used by over 1.3 billion people worldwide. Windows provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to interact with their computers using a mouse and keyboard.
What is top use cases of windows?
The top use cases of Windows include:
- Personal computing: Windows is commonly used for personal computing tasks such as web browsing, document editing, multimedia playback, and gaming.
- Business productivity: Many businesses use Windows for their day-to-day operations, including email management, data analysis, and collaboration tools.
- Software development: Windows provides a platform for software developers to create and test applications, with various development tools and frameworks available.
- Server infrastructure: Windows Server is used for setting up server machines that handle network and data storage operations in businesses and organizations.
What are feature of windows?
Windows includes a wide range of features, including:
- Graphical user interface (GUI): Windows provides a GUI that allows users to interact with their computers using a mouse and keyboard.
- Multitasking: Windows allows users to run multiple programs at the same time.
- File management: Windows includes a file manager that allows users to manage their files and folders.
- Networking: Windows includes built-in networking support that allows users to connect to other computers and networks.
- Security: Windows includes a variety of security features to protect users from viruses, malware, and other threats.
- Accessibility: Windows includes a variety of accessibility features to help people with disabilities use their computers.
What is the workflow of windows?
The workflow of Windows involves the following steps:
- Booting up: After turning on the computer, Windows loads the necessary system files and starts the operating system.
- Login: Users need to provide their credentials to log into their Windows account.
- Desktop: Upon logging in, users are presented with the Windows desktop, where they can access various applications and files.
- Launching applications: Users can launch applications either from the desktop, start menu, or through shortcuts.
- Interacting with applications: Users can perform various tasks using applications, such as creating documents, browsing the internet, or editing multimedia files.
- File management: Users can organize, create, copy, move, and delete files and folders using the file explorer.
- Shutting down: Users can shut down or restart their computer when they are done using Windows.
How windows Works & Architecture?
Windows Architecture:
Windows uses a layered architecture, meaning that it is divided into different layers, each of which has a specific function. This makes it more modular and easier to maintain. The two main layers in Windows are:
User mode: This layer contains all of the programs and services that you use on a daily basis, such as web browsers, word processors, and games. User-mode programs have limited access to system resources and must interact with the kernel mode through system calls.
Kernel mode: This layer is responsible for managing the hardware and system resources of the computer. It also provides services to user-mode programs, such as memory management, file system access, and networking. Kernel-mode programs have full access to system resources and can run at any time.
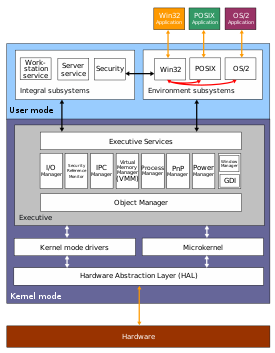
How Windows OS Works:
When you turn on your computer, the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) loads the Windows bootloader. The bootloader then loads the Windows kernel into memory. The kernel then initializes the hardware and system resources, and then loads the user-mode programs that you have configured to start up automatically.
Once the kernel is running, it manages the execution of all of the programs on your computer. It does this by scheduling each program to run for a short period of time, and then switching to the next program in the queue. This process is known as context switching.
The kernel also provides services to user-mode programs, such as memory management, file system access, and networking. User-mode programs can request these services by making system calls.
How to Install and Configure windows ?
To install Windows, you will need a valid Windows product key and a bootable Windows installation medium, such as a USB drive or DVD.
Example:
Suppose you want to install Windows 11 on a new computer with a USB drive containing the Windows 11 installation media.
- Insert the USB drive into your computer and restart it.
- Boot from the USB drive. To do this, you may need to change the boot order in your computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings.
- Once you have booted from the USB drive, you will see the Windows Setup screen.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to install Windows.
Configuring Windows:
Once Windows is installed, you will need to configure it to your liking. This includes setting up your user account, choosing your privacy settings, and installing any applications you need.
Example:
To set up your user account:
- Click the “Next” button on the Welcome screen.
- Select your region and language settings, and then click “Next.”
- Enter a username and password for your user account.
- Click “Next” to create your user account.
To choose your privacy settings:
- Click the “Start” menu and select “Settings.”
- Click “Privacy & security.”
- Review the different privacy settings and adjust them to your liking.
To install applications:
- Open the Microsoft Store.
- Search for the application you want to install and click on it.
- Click the “Get” button to install the application.
Additional configuration tips:
- Enable Windows updates to keep your system secure and up-to-date.
- Install antivirus software to protect your computer from malware.
- Create a backup of your important files.
- Customize your desktop and taskbar to your liking.
Example:
To enable Windows updates:
- Open the Settings app.
- Click “Update & Security.”
- Click “Check for updates.”
- If there are any updates available, click “Download and install.”
To install antivirus software:
- Go to the website of your favorite antivirus software provider.
- Download the antivirus software installation file.
- Run the installation file and follow the on-screen instructions to install the antivirus software.
To create a backup of your important files:
- Open the Control Panel.
- Click “System and Security.”
- Click “File History.”
- Click “Select a drive” and select the drive where you want to store your backups.
- Click “Turn on.”
To customize your desktop and taskbar:
- Right-click on the desktop and select “Personalize.”
- Click on “Themes” to change the theme of your desktop.
- Click on “Start” to customize the Start menu.
- Click on “Taskbar” to customize the taskbar.